React重渲染
简介
react组件在触发了重渲染条件之后,render函数会被再次调用渲染出另外一棵树,接着,React会用对两棵树进行对比,利用diff算法找到需要更新的地方批量改动。
Diff 算法
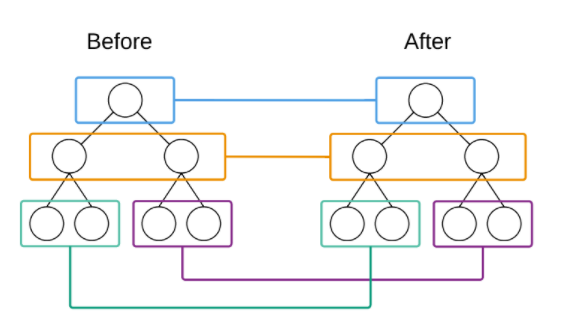
这个过程中,比较两棵Dom tree高效找出需要更新的地方是很重要的。React基于两个假设:
- 两个相同的组件产生类似的DOM结构,不同组件产生不同DOM结构
- 对于同一层次的一组子节点,它们可以通过唯一的id区分
如果父节点不同,React将不会在去对比子节点。因为不同的组件DOM结构会不相同,所以就没有必要在去对比子节点了。这也提高了对比的效率,将算法复杂度从O(n^3)降低到O(n)
为什么是O(n^3)降低到O(n)
- O(n^3): 将两个DOM树的所有节点两两对比,时间复杂度 O(n^2);再进行树的编辑(插入、替换、删除)需要遍历一次,因此时间复杂度为 O(n^3)
- O(n): React Diff算法将所有的节点按层级比较,而且同级节点用唯一id区分,只会遍历一次
class组件重渲染机制
this.setState:
无条件重渲染,不进行新旧比较
this.forceUpdate
无条件重渲染,不进行新旧比较
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| import React from 'react'
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 1
}
handleSetState = () => {
const { count } = this.state
this.setState({ count: count + 1 })
}
handleForceUpdate = () => {
this.forceUpdate()
}
render() {
const { count } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h1>class 组件</h1>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={this.handleSetState}>change state</button>
<button onClick={this.handleForceUpdate}>forceUpdate</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
|
父组件重渲染
父组件重渲染 (用set函数更新状态) 会导致所有子组件重渲染,不管有没有props传递给子组件
优化方法:
- 用React.PureComponent包裹子组件,让子组件只在传入自身的props改变时重渲染
- 加上shouldComponentUpdate对组件真正关注的props进行判断,可避免不必要的重渲染
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
import React from 'react';
import Child from './Child'
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 1,
age: 1,
}
handleSetState = () => {
const { count } = this.state
this.setState({ count: count + 1 })
}
handleSetAge = () => {
const { age } = this.state
this.setState({ age: age + 1 })
}
render() {
const { count, age } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h1>class 组件</h1>
<p>{count}</p>
<button onClick={this.handleSetState}>change count</button>
<button onClick={this.handleSetAge}>change age</button>
<Child age={age} count={count} />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;
import React, { useEffect } from 'react';
class Child extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if (nextProps.count === this.props.count) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('child update')
}
render() {
const { count } = this.props
return (
<div>
<h1>child 组件</h1>
<p>{count}</p>
</div>
)
}
}
export default Child;
|
祖先组件context变动
Context.Provider组件value值的变化会导致Context.Provider下的所有子组件重渲染
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
import React, { createContext } from 'react';
import Child from './Child'
export const Context = createContext();
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
theme: 'red',
}
switchTheme = theme => {
this.setState({theme});
}
render() {
return (
<Context.Provider value={{theme: this.state.theme, switchTheme: this.switchTheme}}>
<h1>class 组件</h1>
<Child />
</Context.Provider>
)
}
}
export default App;
import React from 'react';
import { Context } from './App'
class Child extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Context.Consumer>
{
({theme, switchTheme}) => {
return (
<>
<h1>child 组件</h1>
<p>{theme}</p>
<button onClick={() => switchTheme('black')}>change theme</button>
</>
)
}
}
</Context.Consumer>
)
}
}
export default Child;
|
Function组件重渲染机制
hook设置状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import React, { useState } from 'react';
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const handleClick = () => {
setCount(count => count + 1)
}
return (
<div className="App">
count: {count}
<br/>
<button onClick={handleClick}>click</button>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
|
父组件重渲染
(用set函数更新状态) 会导致所有子组件重渲染,不管有没有props传递给子组件
优化方法:
- React.memo是对props进行浅比较,基本类型(string、number等)直接比较值是否相等,引用类型(object、array)只比较引用是否一致
- 依赖项不变时,React.useCallback能保持函数的引用不变
- 依赖项不变时,React.useMemo能保持引用类型的引用不变
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
import React, { useState, useMemo, useCallback } from 'react'
import Child from './Child'
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const handleClick = useCallback(() => {
setCount(count => count + 1)
}, [])
const objectData = React.useMemo(
() => ({
text: count,
done: false,
}),
[count]
)
return (
<div className="App">
count: {count}
<br/>
<button onClick={handleClick}>click</button>
<Child count={count} age={age}></Child>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
import React, { useEffect, memo } from 'react';
const Child = useMemo(({
count
}) => {
useEffect(() => {
console.log('child update')
})
return (
<div className="child">
{count}
</div>
);
})
export default Child;
|
幸运的是 React.memo 接受第二个参数,用于自定义控制如何比较属性相等
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| const Child = React.memo(
function Child(props: { item: Item }) {
console.log("render child")
const { item } = props
return <div>name:{item.text}</div>
}, (prev, next) => {
return deepEqual(prev, next)
})
|
祖先组件context变动
Context.Provider组件value值的变化会导致Context.Provider下的所有子组件重渲染
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
import React, { createContext, useState, useCallback } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import Child from './Child'
export const Context = createContext();
function App() {
const [theme, setTheme] = useState('red')
const switchTheme = useCallback(theme => {
setTheme(theme);
}, [])
const [age, setAge] = useState(0)
return (
<Context.Provider value={theme}>
<div className="App">
<p>App</p>
{age}
<button onClick={() => setAge(age + 1)}>change theme</button>
<br/>
<button onClick={() => switchTheme('black')}>change theme</button>
<Child></Child>
</div>
</Context.Provider>
);
}
export default App;
import React, { useEffect, useContext } from 'react';
import { Context } from './App'
const Child = () => {
const theme = useContext(Context);
useEffect(() => {
console.log('child update')
})
return (
<div className="child">
{theme}
</div>
);
}
export default React.memo(Child);
|